3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has been a game-changer in various industries, and in 2025, its impact is more significant than ever. This technology allows for the creation of complex, customized objects by layering materials based on digital designs. From manufacturing to healthcare, 3D printing is enabling innovation and efficiency like never before. The advancements in 3D printing technology in 2024 are making it more accessible, affordable, and versatile, opening up new possibilities for businesses and individuals alike.
In the manufacturing sector, 3D printing is revolutionizing production processes. Companies can now create prototypes and products faster and at a lower cost compared to traditional methods. This is particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and customization are critical. For example, aerospace companies are using 3D printing to produce lightweight, complex components that are not possible with traditional manufacturing techniques. This not only reduces the weight of aircraft, leading to fuel savings, but also improves performance and durability.
The automotive industry is also benefiting from 3D printing. Car manufacturers are using the technology to produce custom parts, reduce production time, and lower costs. For instance, companies like BMW and Ford are using 3D printing to create prototypes, tooling, and even end-use parts for their vehicles. This allows them to iterate designs quickly and bring new models to market faster. Additionally, 3D printing is enabling the production of spare parts on demand, reducing the need for large inventories and minimizing waste.
One of the key advantages of 3D printing is its ability to reduce waste by using only the necessary materials. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve cutting away excess material, leading to significant waste. In contrast, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using only the material needed for the final product. This makes 3D printing a more sustainable option, particularly in industries where material costs are high.
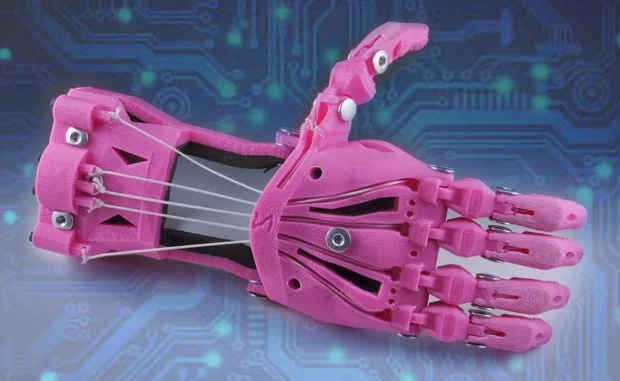
Healthcare is another area where 3D printing is making waves. In 2025, the technology is being used to create customized prosthetics, dental implants, and even organs. For instance, 3D-printed prosthetics are tailored to fit individual patients, improving comfort and functionality. This is particularly beneficial for children, who often outgrow their prosthetics and need frequent replacements. With 3D printing, prosthetics can be produced quickly and at a lower cost, making them more accessible to those in need.
Dental implants are another application of 3D printing in healthcare. Dentists are using the technology to create custom crowns, bridges, and aligners that fit perfectly with a patient’s teeth. This not only improves the quality of dental care but also reduces the time and cost associated with traditional methods. In 2025, 3D printing is becoming a standard tool in dental practices, enabling more efficient and personalized treatments.
Perhaps the most exciting application of 3D printing in healthcare is in the field of regenerative medicine. Researchers are exploring the use of 3D printing to create bioengineered tissues and organs, potentially addressing the shortage of donor organs. For example, scientists are using 3D printing to create scaffolds that can be seeded with a patient’s own cells to grow new tissues. While this technology is still in its early stages, it holds immense promise for the future of medicine.
Despite its numerous benefits, 3D printing also faces challenges. The cost of 3D printers and materials can be prohibitive for some businesses and institutions. Additionally, there are concerns about the quality and durability of 3D-printed products, particularly in critical applications like healthcare. Ensuring that 3D-printed medical devices meet regulatory standards is a significant challenge that needs to be addressed. However, as technology advances and becomes more affordable, these challenges are expected to be overcome.
The integration of 3D printing with other emerging technologies is also driving innovation. For example, the combination of 3D printing and artificial intelligence (AI) is enabling more sophisticated and efficient production processes. AI algorithms can optimize designs for 3D printing, reducing material usage and improving performance. Additionally, the use of advanced materials, such as biocompatible polymers and metals, is expanding the applications of 3D printing in healthcare and other industries.
As we look to the future, the potential of 3D printing to transform industries is undeniable. In 2025, 3D printing is no longer a niche technology; it is a mainstream tool that is driving innovation across industries. From manufacturing to healthcare, the applications of 3D printing are vast and varied. As businesses and researchers continue to explore its potential, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications of 3D printing in the future.
In conclusion, 3D printing is a powerful technology that is transforming industries like manufacturing and healthcare in 2025. Its ability to create complex, customized objects quickly and at a lower cost is revolutionizing production processes and improving patient care. While there are challenges to overcome, the advancements in 3D printing technology are making it more accessible and impactful than ever before. As we continue to explore the possibilities of 3D printing, we can expect to see even more exciting developments that will shape the future of manufacturing, healthcare, and beyond.